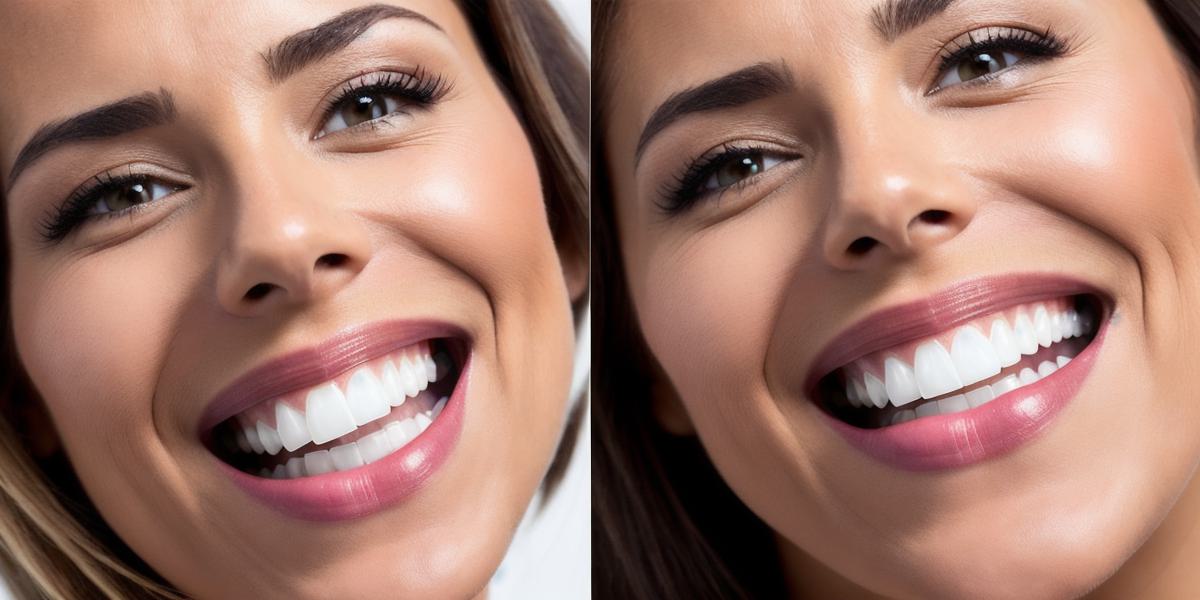
Gum disease is a serious dental problem that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the most common symptoms of gum disease is receding gums, which occur when the gum tissue around your teeth pulls away from them, exposing more of the tooth’s surface. While receding gums may not always be a serious issue, they can increase the risk of other dental problems such as tooth decay and gum disease. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, treatments, and prevention techniques for receding gums.
Causes of Receding Gums
Receding gums can have various causes, including:
- Genetics: Some people are more likely to develop receding gums due to their genetic makeup.
- Gum Disease: Untreated gum disease can cause the gum tissue around your teeth to pull away, resulting in receding gums.
- Ageing: As we age, our gums tend to shrink, which can lead to receding gums.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and using other tobacco products can damage the gum tissue and cause it to recede.
- Brushing Technique: Improper brushing techniques or using hard-bristled toothbrushes can damage the gum tissue, leading to receding gums.
- Hormonal Changes: During menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, hormonal changes can cause gum tissue to recede.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, vitamin C deficiency, and Down syndrome can increase the risk of receding gums.
- Teeth Grinding: Regularly grinding your teeth can put pressure on your gums, causing them to recede.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
Receding gums may not always cause any noticeable symptoms, but some people may experience the following:
- Exposed Tooth Roots: The most visible symptom of receding gums is exposed tooth roots.
- Gum Sensitivity: Receding gums can make your teeth more sensitive to hot and cold temperatures.
- Bad Breath: In some cases, receding gums can cause bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth.
- Bleeding Gums: Receding gums may bleed during brushing or flossing.
- Tooth Decay: Receding gums can increase the risk of tooth decay, as more of your teeth’ surface is exposed to plaque and bacteria.
Treatments for Receding Gums
While receding gums cannot be reversed completely, there are several treatments available that can help slow down or stop the process:
- Professional Cleaning: Regular professional cleaning by a dental hygienist can remove buildup and prevent further damage to your gum tissue.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This procedure involves removing tartar and plaque from the root surface of your teeth, which can help prevent further gum recession.
- Gum Grafts: In some cases, a small amount of healthy gum tissue may be taken from another area in your mouth and used to cover the exposed tooth root. This procedure can help slow down or stop the receding process and improve the appearance of your smile.
- Periodontal Surgery: In severe cases, periodontal surgery may be necessary to remove damaged gum tissue and reshape the surrounding area.
- Mouthwash: Certain mouthwashes containing antiseptics and antibiotics can help reduce inflammation and prevent further gum recession.
- Dental Crown Protection: In some cases, a dental crown or resin coating may be applied to the exposed root surface of the tooth to protect it from further damage and prevent gum recession.
- Dietary Changes: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products can help maintain healthy gums and prevent gum disease.
- Fluoride Treatment: Using fluoride toothpaste or receiving fluoride treatments from your dentist can help strengthen your teeth’ enamel and reduce the risk of receding gums.
Prevention Techniques for Receding Gums
To prevent receding gums, it’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene and avoid habits that can damage your gum tissue:
- Brush Your Teeth: Brush your teeth for at least two minutes twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle pressure.
- Floss Daily: Floss daily to remove plaque and debris from the spaces between your teeth.
- Mouthwash: Use mouthwash as directed to help reduce inflammation and prevent gum disease.
- Avoid Tobacco: Smoking and using other tobacco products can damage your gum tissue and increase your risk of gum disease.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can weaken your gums and increase your risk of gum disease.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can weaken your gums and increase your risk of gum disease.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleaning and checkups to detect any signs of gum recession early.
- Dietary Changes: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products can help maintain healthy gums and prevent gum disease.
Summary
Receding gums are a common dental problem that requires prompt attention and treatment. While the process of regrowing gum tissue is limited, with proper care and treatment, you can help slow down or stop the receding process and improve the appearance of your smile. It’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene, eat a balanced diet, and seek professional dental care if you notice any signs of gum recession. With the right treatments and care, you can enjoy a healthy smile for years to come.



